3d Max Vray Realistic Render Settings
Jun 24, 2015 - What, in your opinion, is the best approach to realistic render? V-Ray 3 – has been created using vray common settings, no tricks neither secret options. I'm Tomasz Wyszolmirski, and I work in Evermotion as 3D artist. About 3 d MAX gamma 2.2 switch, has always been intertwined, inaccurate after. May 2, 2019 - VRaySchool provides an assortment of V-Ray tutorials to help you. Interior Modeling, Lighting & Rendering in 3ds Max and VRay 3.6. Setting the perfect white balance while rendering has always been a tricky affair.
An advanced guide to the interior rendering of still images within Chaos Group Vray and Autodesk 3ds Max. Most will argue that there are no “universal settings” for Vray and I tend to agree. But there are steps you can take in order to get close to what you need for the majority of interior visualisation.There are many other guides out there that offer similar and different approaches to Vray rendering but I have found some techniques to be somewhat confusing and hard to follow. This guide is a summary of all those different techniques, and it will give you rendering settings that work well for interior visualisation as well as the reasons behind them.Before I start, I would like to point out that I will be using a linear workflow with a gamma 2.2 setup within 3ds Max and Vray.
Vray Settings Interior
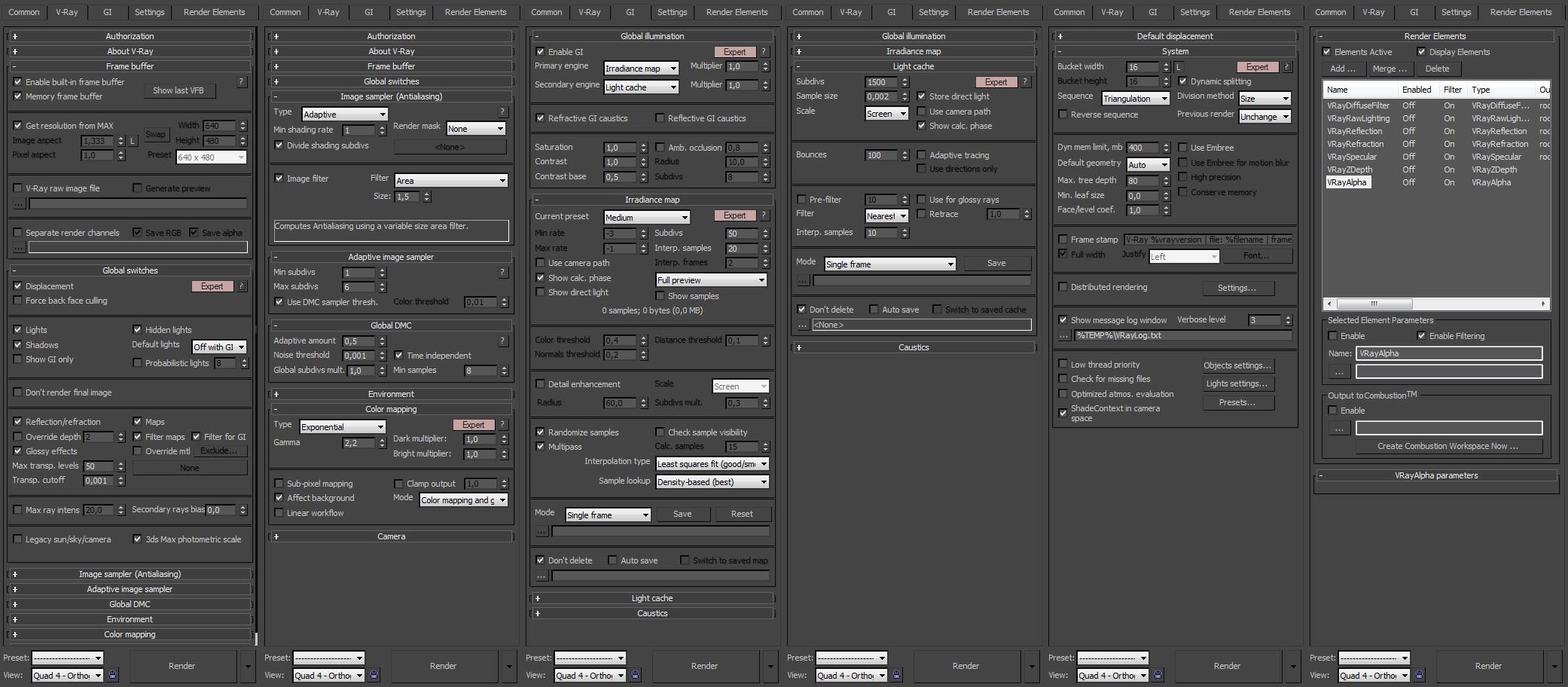
I strongly recommend setting this up as it will improve many areas within your workflow. You can find an easy to follow step by step guide.I also use the Vray physical camera, information on how to set the camera up correctly can be found.Please click on any of the links at the top of the page to jump to a specific section within this post.The initial set upIn the Vray Render Setup go to Vray frame buffer and tick enable built-in frame buffer and leave the other settings as they are. The Vray Frame Buffer has some which will help you finalise your render. At this point you can also tick split render channels and point to the location where you want to save your render passes.In Vray Global Switches, under lighting, set default lights to off. This turns off the 3 point lighting system Autodesk 3ds Max has as default, now you have full control over all lights that you add to the scene.You can also turn displacement off (Optional). Under the geometry rollout, by default displacement is ticked by default, rarely do I have a project where displacement is used so I turn this off. Another personal reason for turning this off is because I work largely with 3rd party CAD data, specifically Autodesk Inventor 3d files which I import into Autodesk 3ds Max.
When working with this file type, leaving this on actually increases render times considerably.It is very important to decide early on the render output size as this influences the time allowed for the project. What resolution do you or your client require? As this largely affects the render settings you decide later on, not matching your output resolution to your render settings can increase your render times unnecessarily. Typically I render out at 3200 pixels x 2400 pixels for A3 presentation, this is large enough to do any post processing, touch ups and if necessary, it can be adjusted for a larger print by lowering the DPI.Anti-aliasingAnti-aliasing works to correct aliasing artefacts which occur within the rendered image either by or of. Aliasing artefacts are generally regarded as jagged edges which are derived from poor, insufficient sampling data.
Which file(s) to download varies from mod to mod, so be sure to read the installation instructions! Once you've found a mod read the description, then click the Files tab. Now you have two ways to download the file. You will now be presented with one or more files, categorized as Main files, Updates, Optional files, Old files, and miscellaneous. From here you can browse the categories, new or newly updated files, top files, use the advanced search, search by tags, or browse the Files of the Month. Fallout 4 manual install mods.

Vray has it’s own method of dealing with Anti-aliasing and this is controlled via the Vray image sampler (Antialiasing) within the render setup.Here is a quick explanation of the types of image sampler, again I am not going to go in to much detail as this is not the main focus of this post but if you wish to know more, you will find an in depth explanation on image sampling.FixedThis is a non-adaptable sampler that uses the simplest method of calculating. Subdivisions determine the number of samples per pixel, 1 sample is equal to 1 pixel (1×1). Whereas 4 samples divides the pixel in to 16 (4×4). The more samples per pixel given improves sampling and therefore results in a better quality render. Negative values are not something to be associated with this sampler.For scenes that have blurry effects and/or detailed textures, the fixed rate sampler performs best but at the cost of a higher render time due to the amount of samples needed to get a passable result.
Because of this it is not recommend for interior visualisation but at a low setting it can be useful for preview renders.Adaptive subdivisionThe first word “adaptive” means that this sampler can adapt to the scene via undersampling and oversampling. By being adaptive in a positive and negative way, Vray can calculate the number of samples needed for areas that are less detailed (undersampling) than more complex areas which require more samples (oversampling).This method does not work well with glossy reflections and camera effects such as depth of field, but instead sits well with flat colour, non-reflective objects which are commonly used in architectural visualisation.Adaptive DMCIn simple terms this is the next step on from the fixed sampler, with the addition of adaptability. It will take a minimum/maximum value of positive subdivisions and calculate the most effective number of samples needed for a given pixel. Much like adaptive subdivision, it will attend more to detailed areas of the scene and pay less attention to the lesser detailed areas.It is the most beneficial solution for both speed and quality when calculating glossy reflections, depth of field (DOF) and so on.
It will be the chosen image sampler for this topic.Choosing the right anti-aliasing filterIn addition to the image sampler, the anti-aliasing filter takes the calculated sub pixels and averages out the colour of all samples that belong to that particular pixel. Each anti-aliasing filter available offers different calculations which in turn produce different results. For example, some filters create a soft blurred effect on the edges of your 3D geometry whereas others produce a hard sharpening, there are also filters that lie in between these two.
3d Max Vray Realistic Render Settings 10

As well as this you have the option to use no filter at all thus allowing you to add your own desired effect in post processing. This can be easily managed for a single image but for an animation it may prove to be difficult to adjust every frame to how you want it.There is no right or wrong filter to choose, it’s down to personal preference. ✖ Legal terms and conditionsLegal disclosuresAutodesk makes software and services available on a licensed or subscription basis. Rights to install, access, or otherwise use Autodesk software and services (including free software or services) are limited to license rights and services entitlements expressly granted by Autodesk in the applicable license or service agreement and are subject to acceptance of and compliance with all terms and conditions of that agreement.
When you subscribe to a plan, it may renew automatically for a fixed fee on a monthly or annual basis, subject to availability. All benefits and purchase options may not be available for all software or services in all languages and/or geographies. Access to cloud services requires an Internet connection and is subject to any geographical restrictions set forth in the Terms of Service.© 2019 Autodesk Inc.
All rights reserved.