Chapter No 72 Of Gst
This article is about the tax. For legislation, see.Goods and Services Tax ( GST) is an (or ) imposed in on the supply of goods and services. It is a comprehensive multistage, destination based tax. Comprehensive because it has subsumed almost all the indirect taxes except few.
Know all about GST tariff for goods, GST tariff for services with their HSN Code & SC. Only five documents can be opened in tabs. If you continue, tabs opened first shall be closed.
Multi-Staged as it is imposed at every step in the production process, but is meant to be refunded to all parties in the various stages of production other than the final consumer. And destination based tax, as it is collected from point of consumption and not point of origin like previous taxes.Goods and services are divided into five different tax slabs for collection of tax - 0%, 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%. However, and are not taxed under GST and instead are taxed separately by the individual, as per the previous tax regime. There is a special rate of 0.25% on rough precious and semi-precious stones and 3% on. In addition a of 22% or other rates on top of 28% GST applies on few items like aerated drinks, and tobacco products. Pre-GST, the statutory tax rate for most goods was about 26.5%, Post-GST, most goods are expected to be in the 18% tax range.The tax came into effect from July 1, 2017 through the implementation of by the.
The tax replaced existing multiple flowing taxes levied by the and governments.The tax rates, rules and regulations are governed by the GST Council which consists of the finance ministers of and all the states. GST is meant to replace a slew of indirect taxes with a federated tax and is therefore expected to reshape the country's 2.4 trillion dollar economy, but not without criticism. Trucks' travel time in interstate movement dropped by 20%, because of no interstate check posts. Contents.History Formation The reform of India's indirect tax regime was started in 1986 by, Finance Minister in ’s government, with the introduction of the Modified Value Added Tax (MODVAT). Subsequently, Prime Minister and his Finance Minister, initiated early discussions on a (VAT) at the state level. A single common 'Goods and Services Tax (GST)' was proposed and given a go-ahead in 1999 during a meeting between the and his economic advisory panel, which included three former RBI governors,.
Vajpayee set up a committee headed by the of, to design a GST model.The Ravi Dasgupta committee which was also tasked with putting in place the back-end technology and logistics (later came to be known as the GST Network, or GSTN, in 2015). It later came out for rolling out a uniform taxation regime in the country. In 2002, the Vajpayee government formed a task force under to recommend tax reforms. In 2005, the Kelkar committee recommended rolling out GST as suggested by the.After the defeat of the -led government in the and the election of a Congress-led government, the new Finance Minister in February 2006 continued work on the same and proposed a GST rollout by 1 April 2010. However, in 2011, with the routing out of power in, Asim Dasgupta resigned as the head of the GST committee. Dasgupta admitted in an interview that 80% of the task had been done.In the, the -led government was elected into power.
With the consequential dissolution of the, the GST Bill – approved by the standing committee for reintroduction – lapsed. Seven months after the formation of the then, the new Finance Minister introduced the GST Bill in the, where the BJP had a majority. In February 2015, Jaitley set another deadline of 1 April 2017 to implement GST. In May 2016, the Lok Sabha passed the Constitution Amendment Bill, paving way for GST.
However, the Opposition, led by the Congress, demanded that the GST Bill be again sent back for review to the Select Committee of the due to disagreements on several statements in the Bill relating to taxation. Finally in August 2016, the Amendment Bill was passed.
Over the next 15 to 20 days, 18 states ratified the Constitution amendment Bill and the President gave his assent to it.A 21-member selected committee was formed to look into the proposed GST laws. After GST Council approved the Central Goods and Services Tax Bill 2017 (The CGST Bill), the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Bill 2017 (The IGST Bill), the Union Territory Goods and Services Tax Bill 2017 (The UTGST Bill), the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to the States) Bill 2017 (The Compensation Bill), these Bills were passed by the Lok Sabha on 29 March 2017. The Rajya Sabha passed these Bills on 6 April 2017 and were then enacted as Acts on 12 April 2017. Thereafter, State Legislatures of different States have passed respective State Goods and Services Tax Bills. After the enactment of various GST laws, Goods and Services Tax was launched all over India with effect from 1 July 2017.
The Jammu and Kashmir state legislature passed its GST act on 7 July 2017, thereby ensuring that the entire nation is brought under an unified indirect taxation system. There was to be no GST on the sale and purchase of securities. That continues to be governed by (STT). Launch The GST was launched at midnight on 1 July 2017 by the President of, and the.
The launch was marked by a historic midnight (30 June – 1 July) session of both the houses of parliament convened at the Central Hall of the Parliament. Though the session was attended by high-profile guests from the business and the entertainment industry including, it was boycotted by the opposition due to the predicted problems that it was bound to lead for the middle and lower class Indians.
Chapter No 72 Of Gst Payment
It is one of the few midnight sessions that have been held by the parliament - the others being the on 15 August 1947, and the and of that occasion. After its launch, the GST rates have been modified multiple times, the latest being on 22 December 2018, where a panel of federal and state finance ministers decided to revise GST rates on 28 goods and 53 services.Members of the boycotted the GST launch altogether.
They were joined by members of the, and the. The parties reported that they found virtually no difference between the GST and the existing taxation system, claiming that the government was trying to merely rebrand the current taxation system. They also argued that the GST would increase existing rates on common daily goods while reducing rates on luxury items, and affect many Indians adversely, especially the middle, lower middle and poorer income groups. Tax Taxes subsumed The single GST subsumed several taxes and levies which included: central excise duty, additional customs duty, state-level and Octroi. Other levies which were applicable on inter-state transportation of goods have also been done away with in GST regime. GST is levied on all transactions such as sale, transfer, purchase, barter, lease, or import of goods and/or services.India adopted a dual GST model, meaning that taxation is administered by both the Union and State Governments. Transactions made within a single state are levied with Central GST (CGST) by the Central Government and State GST (SGST) by the State governments.
For inter-state transactions and imported goods or services, an Integrated GST (IGST) is levied by the Central Government. GST is a consumption-based tax/destination-based tax, therefore, taxes are paid to the state where the goods or services are consumed not the state in which they were produced. IGST complicates tax collection for State Governments by disabling them from collecting the tax owed to them directly from the Central Government.
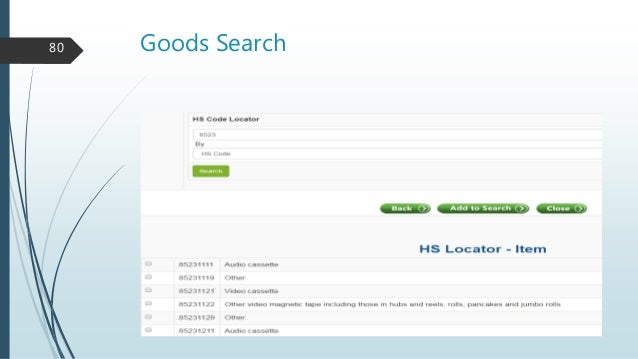
Under the previous system, a state would only have to deal with a single government in order to collect tax revenue. HSN code HSN is an 8-digit code for identifying the applicable rate of GST on different products as per CGST rules. If a company has turnover up to ₹1.5 Crore in the preceding financial year then they need not mention the HSN code while supplying goods on invoices. If a company has turnover more than ₹1.5 Crore but up to ₹5 Cr then they need to mention the first two digits of HSN code while supplying goods on invoices. If turnover crosses ₹5 Cr then they shall mention the first 4 digits of HSN code on invoices. Rate The GST is imposed at variable rates on variable items. The rate of GST is 18% for soaps and 28% on washing detergents.
GST on movie tickets is based on slabs, with 18% GST for tickets that cost less than Rs. 100 and 28% GST on tickets costing more than Rs.100 and 5% on readymade clothes.
The rate on under-construction property booking is 12%. Some industries and products were exempted by the government and remain untaxed under GST, such as dairy products, products of milling industries, fresh vegetables & fruits, meat products, and other groceries and necessities.Checkposts across the country were abolished ensuring free and fast movement of goods.The Central Government had proposed to insulate the revenues of the States from the impact of GST, with the expectation that in due course, GST will be levied on petroleum and petroleum products. The central government had assured states of compensation for any revenue loss incurred by them from the date of GST for a period of five years.
However, no concrete laws have yet been made to support such action. GST council adopted concept paper discouraging tinkering with rates. E-Way Bill An e-Way Bill is an electronic permit for shipping goods similar to a. It was made mandatory for inter-state transport of goods from 1 June 2018. It is required to be generated for every inter-state movement of goods beyond 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) and the threshold limit of ₹50,000 (US$720).It is a, technology solution and critical tool to check tax leakages and clamping down on trade that currently happens on a cash basis.
The pilot started on 1 February 2018 but was withdrawn after glitches in the GST Network. The states are divided into four zones for rolling out in phases by end of April 2018.A unique e-Way Bill Number (EBN) is generated either by the supplier, recipient or the transporter. The EBN can be a printout, SMS or written on invoice is valid. The GST/Tax Officers tally the e-Way Bill listed goods with goods carried with it. The mechanism is aimed at plugging loopholes like overloading, understating etc. Each has to be matched with a GST invoice.Transporter ID and PIN Code now compulsory from 01-Oct-2018.It is a critical compliance related GSTN project under the GST, with a capacity to process 75 lakh e-way bills per day.Intra-State e-Way Bill The five states piloting this project are Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Kerala, Telangana and Uttar Pradesh, which account for 61.8% of the inter-state e-way bills, started mandatory intrastate e-way bill from 15 April 2018 to further reduce tax evasion. It was successfully introduced in Karnataka from 1 April 2018.
The intrastate e-way bill will pave the way for a seamless, nationwide single e-way bill system. Six more states Jharkhand, Bihar, Tripura, Madhya Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Haryana will roll it out from 20 April 18. All states are mandated to introduce it by May 30, 2018.Reverse Charge Mechanism Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) is a system in GST where the receiver pays the tax on behalf of unregistered, smaller material and service suppliers. The receiver of the goods is eligible for, while the unregistered dealer is not.In the notification dated on 29 January 2019, the Indian government has finally implemented the RCM (reverse charge mechanism) which started from 1 February 2019 as per the GST acts and amendments. Also to note that the up to INR 5000 exemptions will be removed effectively. Goods kept outside the GST. Alcohol for human consumption.
Petrol and petroleum products (GST will apply at a later date) viz. Petroleum crude, High speed diesel, Motor Spirit (petrol), Natural gas, Aviation turbine fuel.GST Council GST Council is the governing body of GST having 33 members.
It is chaired by the Union Finance Minister. GST Council is an apex member committee to modify, reconcile or to procure any law or regulation based on the context of goods and services tax in India.
The council is headed by the union finance minister assisted with the of all the states of India. The GST council is responsible for any revision or enactment of rule or any rate changes of the goods and services in India.Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) The GSTN software is developed by and the Information Technology network that provides the computing resources is maintained by the. 'Goods and Services Tax' Network (GSTN) is a nonprofit organisation formed for creating a sophisticated network, accessible to stakeholders, government and taxpayers to access information from a single source (portal). The portal is accessible to the Tax authorities for tracking down every transaction, while taxpayers have the ability of connect for their tax returns.The GSTN's authorised capital is ₹10 crore (US$1.4 million) in which initially the Central Government held 24.5 percent of shares while the state government held 24.5 percent. The of this section is. Relevant discussion may be found on the.
Please do not remove this message until. ( November 2018) Technicalities of GST implementation in India have been criticized by global financial institutions, sections of Indian media and opposition political parties in India. 2018 version of India Development Update described India's version of GST as too complex, noticing various flaws compared to GST systems prevalent in other countries; most significantly, the second highest tax rate among a sample of 115 countries at 28%.GST's implementation in India has been further criticized by Indian businessmen for problems including tax refund delays and too much documentation and administrative effort needed. According to a partner at, when the first GST returns were filed in August 2017, the system crashed under the weight of filings.The opposition has consistently been among the most vocal opponents of GST implementation in India with party President, and leader of the opposition, slamming for allegedly 'destroying small businessmen and industries' in the country.
He went on to pejoratively dub GST as after an ill-famed, fictional dacoit in Bollywood films. Blaming the implementation of gst as a 'way of removing money from the pockets of the poor', Rahul has lamented it as a 'big failure' while declaring that if Congress Party is elected to power, it will implement a single slab GST instead of different slabs.In the run-up to the, Rahul has intensified his 'Gabbar Singh' jibes on Modi government. See also.Notes. Retrieved 30 June 2017., 18 May 2017. Retrieved 3 July 2017., 31 March 2017.
^, 29 June 2017., 29 June 2017., 29 June 2017. Nair, Remya (8 June 2015),., 22 June 2017., 27 November 2016., Financial Express, 30 June 2017. ^, 30 June 2017.,.
PTI (30 June 2017). Retrieved 22 January 2018., 29 June 2017., 17 April 2017., 20 September 2016., 30 November 2016., 30 January 2017. Money Control. Masters India. Mehra, Puja (27 June 2017).
The Hindu - Opinion. Retrieved 3 July 2017., 5 July 2017.
The Indian Express. 30 June 2017. Retrieved 30 July 2017., 4 July 2017. Newindianexpress.com.
Sikarwar, Deepshikha (9 October 2017). Fallout new vegas dlc maps games. The Economic Times. Retrieved 9 October 2017., 25 January 2018.
The Times of India. Times of India.
Retrieved 6 February 2018. Telegraphindia.com. ^,. E-Startup India. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
^, 27 February 2018., 1 November 2018. ^. ^.

Accaglobal.com. ^. Bureau, Our. The Times of India.External links.
Date: Trade Notice 20/2019-20Date: PUBLIC NOTICE NO. 13/(2015-2020)Date: Notification No. 46/2019-CUSTOMS (N.T.)Date: PUBLIC NOTICE No. 12/2015-2020Date: Circular No. 1070/3/2019 CXDate: Notification No. 26 /2019-Customs (ADD)Date: Notification No. 25/2019-Customs (ADD)Date: Notification No.
25 /2019 – Central TaxDate: TRADE NOTICE NO. 19/2019-2020Date: Notification No.45/2019 - Customs (N.T.).